Clinical manifestation and diagnosis of leishmaniasis
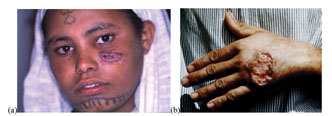
The clinical presentation of the two forms of leishmaniasis are very different. Cutaneous leishmaniasis normally produces skin ulcers on the exposed parts of the body such as the face, arms and legs (figure below). The disease can produce a large number of ulcers – sometimes up to 200 – which may result in physical disability (e.g. in using the hands). The visible ulcers are a source of social stigma, which can leave the patient suffering mental distress and rejection in their community.
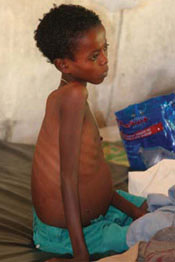
Visceral leishmaniasis (also known as kala azar, which means black fever in Hindu) is a life-threatening disease characterised by irregular episodes of fever, rapid and extensive weight loss, huge swelling of the spleen and liver (figure below), and anaemia. If left untreated, up to 100% of patients die within two years of infection. For this reason, visceral leishmaniasis is said to have a high case-fatality rate.
You can identify patients with leishmaniasis by the clinical manifestations of the disease. For confirmation of the diagnosis, laboratory investigations should be done in higher health facilities or hospitals, where the protozoan parasites can be detected in blood smears viewed with a microscope.