Focused Assessment of the Renal System
Focused Assessment of the Renal System
1. History
Some of the renal or urinary system-focused questions that you should ask the patient include:
- Do you urinate more than usual? (frequency, urgency, nocturia)
- Any pain or burning upon urination?
- Any difficulty starting or maintaining the stream of urine?
- Ask about changes in urine color: Any blood in your urine?
- Any difficulty controlling your urine?
2. Physical Examination
Inspection
- Client's general appearance and assessment of mental status.
- The client's hydration status and skin color provide data about the function of the urinary system.
- The renal arteries are auscultated for bruits.
- The costovertebral angles and flanks are inspected for color, symmetry, and masses
- Assess skin turgor for dehydration, which may accompany diabetes or diuretic use.
- Palpate abdomen for bladder distention.
- Inspect urine specimen for color and odor and presence of blood in urine
- See for orbital and pre tibia edema,.
Palpation
Palpate to see for orbital and per tibia edema
Palpation for the kidneys- It should be noted that a kidney does not move discernibly on inspiration and if significantly enlarged, may be bimanually palpable i.e. it can be "bounced" between your hands.
- To examine for the kidneys, one hand should be placed on the abdomen and should remain fixed; the other hand is then placed posteriorly, and is used to 'flick' the kidney between your hands.
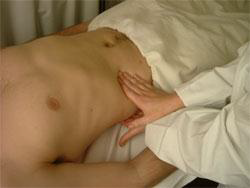
The kidneys are not easily palpated except in the presence of enlargement or disease
Palpation of the costovertebral angle and flanks reveals tenderness or masses
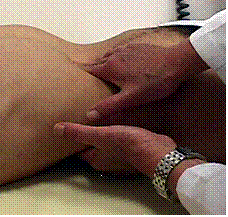
- Search for right kidney as the left normally not palpable.
- Place hand under patient's right kidney, feel with opposite hand on abdomen (hands in "duck-bill" position) Press 2 hands together firmly, ask patient to take deep breath, you feel no change.
- Costo-Vertebral Angle (CVA) - tenderness
- Place ball of hand at CVA, strike it with ulnar surface of right (Sharp pain occurs with inflammation
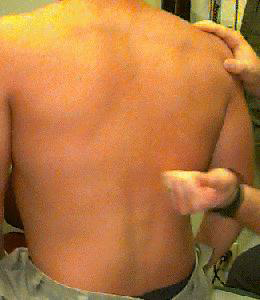
Percussion
Blunt percussion at the costovertebral angle produces pain or discomfort in the presence of kidney disease. Percussion above the symphysis pubis is carried out to determine the location and degree of fullness of the bladder.
Investigations
Order urine analysis, renal function test (BUN/creatinine and serum electrolytes) and if patient is on diuretics or decreased urine output add electrolytes and communicate or consult physician accordingly.