Cataract
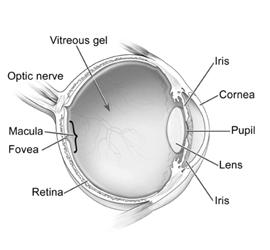
Cataract is clouding of the lens of the eye which leads to a decrease in vision. It is the most common cause of blindness.
Visual loss occurs because opacification of the lens blocks light from passing and being focused on the retina at the back of the eye. Although most cases of cataract are related to the ageing process, occasionally children can be born with the condition, or a cataract may develop after eye injuries, inflammation, and some other eye diseases. Persons with cataract experiences reduction of vision and complains of glare
Epidemiology
Cataract remains the leading cause of blindness in both developed and developing countries. According to the latest assessment, cataract is responsible for nearly 51% of world blindness, which represents about 20 million people. Although cataracts can be surgically removed, in many countries barriers exist that prevent patients from accessing surgery.
As people in the world live longer, the number of people with cataract is anticipated to grow. If cataract left un-treated, it would make persons totally blind and disabled. Since their activity and body movement is limited, this will cause passive contracture, less productive, dependency, psychological and social stress
Prevention and treatment of cataracts
Risk reduction (reduction of cigarette smoking and ultraviolet light exposure) may prevent or delay the development of cataract. Diabetes mellitus and high body mass index ( obesity) are identified as additional risk factors. The treatment of cataract is surgical and very successful in restoring sight. The opaque lens is removed and replaced by an artificial intraocular lens. In many remote parts of the developing world, people remain blind from cataract, due to a lack of access to eye care.
As a health extension worker, you are responsible searching and referring cases remain at their home because of visual disability due to cataract. In addition to case detection activity, you are expected to teach your community about risk reduction strategies to prevent cataract, such as preventing obesity (dietary habits and exercise), avoid smoking and exposure to ultraviolet light ( use of dark eye glass), appropriate, timely intervention for any eye injury and infections.
N.B.: Vision 2020 is a global initiative that aims to eliminate avoidable blindness by the year 2020. It was launched on 18 February 1999 by the World Health Organization together with the more than 20 international non-governmental organisations involved in eye care and prevention and management of blindness that comprise the International Agency for the Prevention of Blindness (IAPB). Vision 2020 is a partnership that provides guidance, technical and resource support to countries that have formally adopted its agenda.