Essential newborn care
Neonatal resuscitation
For some babies, the need for resuscitation may be anticipated:
- Those born to mothers with chronic illness, where the mother had a previous foetal or neonatal death.
- A mother with pre-eclampsia.
- In multiple pregnancies, in preterm delivery, in an abnormal presentation of the foetus, a prolapsed cord,
- A prolonged labour or rupture of membranes or meconium-stained liquor.
However, for many babies, the need for resuscitation cannot be anticipated before delivery. Therefore, be prepared for resuscitation at every delivery. First, observe quickly for any signs of respiratory problems:
- Having difficulty in breathing or signs of gasping (shortage of breathing).
- Breathing less than 30 breaths per minute or not breathing at all.
- The skin becomes cyanotic because of deficiency of oxygen.
If the baby needs resuscitation, quickly clamp or tie and cut the cord, leaving a stump at least 10 cm long for now and then start resuscitation immediately by using the correct size of the face mask.
| Position |
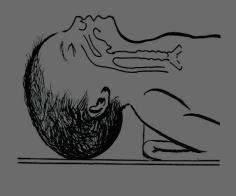
Correct position 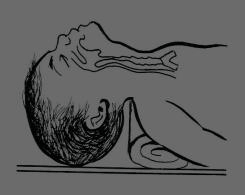
Hyper flexed incorrect position 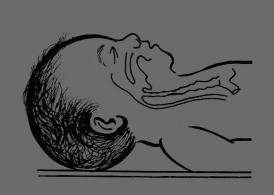
Hyperextended wrong position |
|---|---|
| Clear airway |
|
| Ventilate |

Correct proper mask 
Incorrect smaller mask 
Incorrect bigger mask. |
| Monitor |
|
How to ventilate:
- Squeeze bag with two fingers or whole hand, 2-3 times.
- Observe for the rise of the chest.
- IF CHEST IS NOT RISING: Reposition the head or Check mask seal.
- Squeeze bag harder with the whole hand.
- Once good seal and chest rising, ventilate at 40 -60 squeezes per minute.
- Squeeze a bag 2-3 times with two fingers and a thumb. (When you press the bag Count 101 for the first Squeeze, 102 for the second Squeeze, 103 for the third Squeeze to deliver the desired amount oxygen).
- Observe the chest while ventilating:
- Is it moving with the ventilation?.
- Is the baby breathing spontaneously?.
When to stop ventilating?:
- When the newborn, breathe spontaneously or cry.
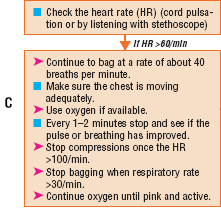
- When the newborn breathing is >30 b/m and regular:
- Continue resuscitation for 20 minutes until the babies spontaneously breathe. After 20 minutes if the newborn is not breathing spontaneously or birthing is weak and irregular you stop ventilation and urgently refer the child to the health centre or hospital.
When to continue ventilating?
- When the newborn breathing is <30 b/m.
- When gasping or breathing is irregular.
- The baby has severe chest in-drawing.

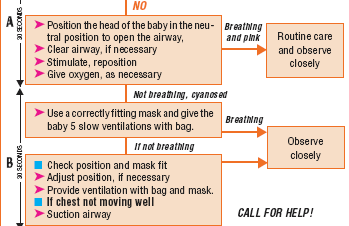
Immediate assessment and newborn care
If you are attending a delivery or a baby is brought to you immediately after birth, you need to dry and wrap the baby with dry cloth and cover the head and assess any breathing problem:
Assessment and classification of newborns
| Signs | Classification |
Treatment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| If any of the following sign is present: |
Birth asphyxia |
Start resuscitation |
|
| Breathing >30 b/m | NO Birth asphyxia |
Continue with the essential newborn care. |