Pupils
The diameter and reactivity to the light of the patient's pupil reflect the status of the brain's perfusion, oxygenation and condition.
On injury, if the pupil reacts in any of the following ways:
- Become fixed with no reaction to light
- Dilate with light and constrict when the light is removed.
- React sluggishly.
- Become unequal in size.
- Become unequal in size when a bright light is introduced into or removed from one eye.
Depressed brain function can be produced by the following situation
- Injury to the brain or brain stem.
- Trauma or stroke.
- Brain tumour.
- Inadequate oxygen perfusion.
- Drugs or toxins (Central nervous system depressant).

Fig. 18. Constricted pupil.
- P = Pupils
- E = Equal
- A = And
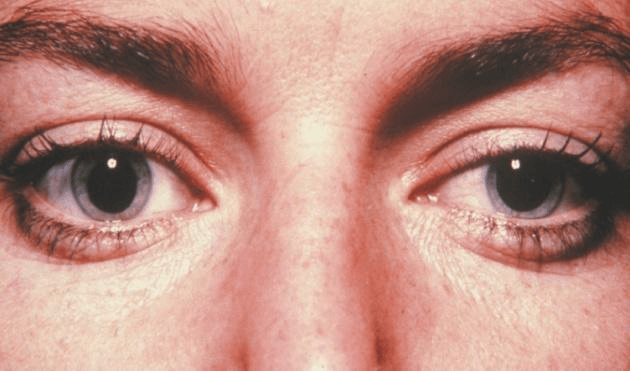
Fig.19. Dilated pupil.
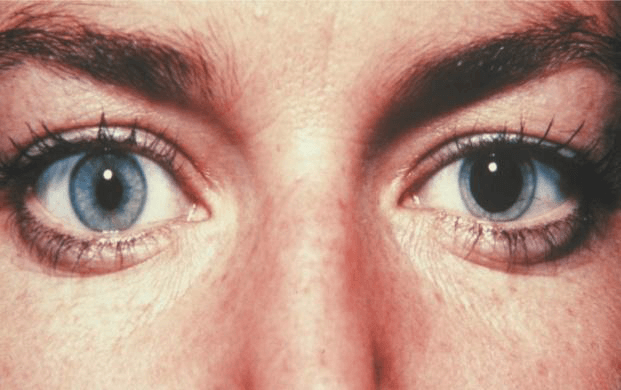
Fig. 20. Unequal size pupil.
The letter PEARRL serves as a useful guide in assessing pupil. They stand for the following:
- R = Round
- R = Regular in size
- L = react to Light
Last modified: Sunday, 13 November 2016, 10:19 AM