Male condom
Male condoms are more prevalent than female condoms. A male condom is a thin sheath that is worn over the man's penis during sexual intercourse. The condom collects sperm so that the sperm are not released into a woman's vagina. Condoms are also called rubbers, sheaths, prophylactics, and many other names. Thus, in this study session, more emphasis will be given to the male condom than to any other barrier method, and you will learn about it in detail. Condoms are the best protection against STIs and HIV. They can be used alone or along with any other family planning method.
Mechanism of Action
The condom must be put on the man's penis when it is hard, but before it touches the woman's genitals. If he rubs his penis on the woman's genitals or goes into her vagina, he can make the woman pregnant or can give her an STI, even if he does not spill his sperm (ejaculate)
How to Use the Condom
- Use a new condom for each act of sex. Check the condom package. Do not use if torn or damaged. Avoid using a condom past the expiration date-do so only if a newer condom is not available. Tear open the package carefully (Figure below). Do not use fingernails, teeth, or anything that can damage the condom

- Before any physical contact, place the condom on the tip of the erect penis with the rolled side out. If the man is not circumcised, pull the foreskin back. Squeeze the tip of the condom and put it on the end of the hard penis. For the most protection put the condom on before the penis makes any genital, oral, or anal contact.
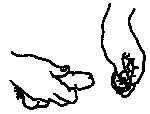
- Keep squeezing the tip while unrolling the condom, until it covers the entire penis. The loose part at the end will hold the man's sperm. If you do not leave space for the sperm when it comes out, the condom is more likely to break
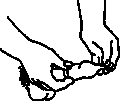
- After the man ejaculates, he should hold on to the rim of the condom and withdraw from the vagina while his penis is still hard.
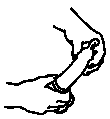
- Take off the condom. Do not let sperm spill or leak. If having sex again or switching from one sex act to another, use a new condom.

- Tie the condom shut and dispose of it away from children and animals.
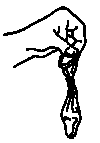
Common Mistakes and Important Messages for Condom Users
The five most common mistakes are:
- Not having a condom when needed.
- Starting intercourse without a condom on the penis, then interrupting intercourse to put on the condom (or deciding not to use the condom at all).
- Tearing the condom with a fingernail.
- Not holding the rim of the condom when withdrawing the penis from the vagina, causing condom slippage and leakage.
- Forgetting to use the condom altogether.
Important
- They should not use two condoms at once. Placing two male condoms on a penis can raise the chance of tearing.
- Used condoms should be thrown away after each sex act.
- Male condoms and female condoms should not be used at the same time.
- The condom must be used from "start to finish" with every act of intercourse.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Male Condom
Advantages:
- If used correctly and consistently with every act of sexual intercourse, help protect against risks of pregnancy, STIs, including HIV
Disadvantages:
Condoms do have some disadvantages. The most common ones are as follows:
- Women have to rely on the man's cooperation to protect themselves from pregnancy and disease.
- Some people connect condoms with immoral sex, sex outside marriage, or sex with prostitutes, and do not want to use them.
- Some people are too embarrassed to buy, ask a partner to use, put on, take off, or throw away condoms.
- Latex condoms may cause itching for a few people who are allergic to latex and/or lubricants.
- There is a small possibility that a condom will slip off during sex.
- Condoms can weaken and may break during use if stored for too long or in too much heat, sunlight or humidity, or if used with oil-based lubricants, such as Vaseline or edible oils.