Is the baby's temperature normal?
Measure the baby's temperature, preferably using a rectal thermometer inserted gently into the baby's rectum through the anus, or use a normal thermometer held closely under the baby's armpit (this is called the axillary temperature). Remember that the thermometer must be very clean before you use it. Wash it before and after use in clean water and then swab it with alcohol or another antiseptic solution. If you do not have a thermometer, use your hand to feel the baby's head and body for fever, or low body temperature, by comparing how the baby feels with the temperature of your own or the mother's skin.
Refer a baby with a fever or hypothermia if its temperature does not return to normal quickly
Fever is defined as a temperature equal to or greater than 37.5ºC. If you suspect that the baby may be too hot because it has been kept too warm by the mother, cool the baby by unwrapping its blankets and measure the temperature again after 15 minutes. If the temperature does not return to normal quickly, or if it is above 37.5ºC, refer the baby immediately. A high temperature is a danger sign for infection, which must be treated quickly.
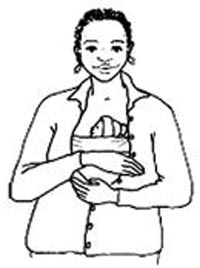
Hypothermia is defined as a temperature of equal to or less than 35.5ºC, but this is dangerously low for a newborn. If the baby feels chilled, don't wait for its temperature to fall lower than 36.5ºC before taking fast action to warm it. Remove the clothes from its body and place it in skin-to-skin contact with the mother, between her breasts and inside her clothes. Wrap them both well with blankets, place a cap or shawl to cover the top and back of the baby's head, and if the baby is not wearing socks, wrap its feet (this is called Kangaroo Mother Care). If the baby's temperature does not start rising towards normal within 30 minutes, or if it is below 35.5ºC, or the baby's lips are blue, refer the baby immediately.
After assessing the newborn baby's vital signs as described above, the next step is to assess for danger signs of newborn illnesses.